skip to main |
skip to sidebar
/* how to open notepad using java program, opening notepad in java code,how to open a text file in java with notepad, how to open notepad through java program */
public calss demo
{
public void note()
{
try {
System.out.print(".....Opening notepad.....");
java.lang.Runtime runTime = java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime();
java.lang.Process process = runTime.exec("notepad");
try {
//notepad will be closed after 5000 ms
java.lang.Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (java.lang.InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Closing notepad");
process.destroy();
} catch (java.io.IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class notepad {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new demo().note();
}
}
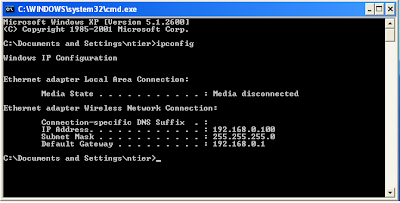
How to run:
javac notepad.java
java notepad
Output:
/* jfreechart bar chart in java swings with example, jfreechart example code in java */
package cost;
import cost.*;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.GradientPaint;
import org.jfree.chart.ChartFactory;
import org.jfree.chart.ChartPanel;
import org.jfree.chart.JFreeChart;
import org.jfree.chart.axis.CategoryAxis;
import org.jfree.chart.axis.CategoryLabelPositions;
import org.jfree.chart.axis.NumberAxis;
import org.jfree.chart.plot.CategoryPlot;
import org.jfree.chart.plot.PlotOrientation;
import org.jfree.chart.renderer.category.BarRenderer;
import org.jfree.data.category.CategoryDataset;
import org.jfree.data.category.DefaultCategoryDataset;
import org.jfree.ui.ApplicationFrame;
import org.jfree.ui.RefineryUtilities;
import java.io.*;
/**
* A simple demonstration application showing how to create a bar chart.
*
*/
public class graph extends ApplicationFrame {
/**
* Creates a new demo instance.
*
* @param title the frame title.
*/
public graph(final String title) {
super(title);
final CategoryDataset dataset = createDataset();
final JFreeChart chart = createChart(dataset);
final ChartPanel chartPanel = new ChartPanel(chart);
chartPanel.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(500, 270));
setContentPane(chartPanel);
}
public String read(String st)
{
String er="";
try
{
File fileDir = new File(st);
BufferedReader in1 = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(fileDir)));
String str;
while ((str = in1.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(str);
er=str;
}
in1.close();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
return er;
}
/**
* Returns a sample dataset.
*
* @return The dataset.
*/
private CategoryDataset createDataset() {
String s1=read("cocomo81.txt");
String s2=read("cocomoa.txt");
String s3=read("cocomoi.txt");
String s4=read("slim.txt");
String s5=read("fp.txt");
String s6=read("algo.txt");
String s7=read("rev.txt");
Anova ano=new Anova();
String tot1=ano.calc("cocomo81.txt");
String tot2=ano.calc("cocomoa.txt");
String tot3=ano.calc("cocomoi.txt");
String tot4=ano.calc("slim.txt");
String tot5=ano.calc("fp.txt");
String tot6=ano.calc("algo.txt");
String tot7=ano.calc("rev.txt");
String total=tot1+"##"+tot2+"##"+tot3+"##"+tot4+"##"+tot5+"##"+tot6+"##"+tot7;
new Store().store(total,"errors.txt");
String s11[]=s1.split("##");
String s21[]=s2.split("##");
String s31[]=s3.split("##");
String s41[]=s4.split("##");
String s51[]=s5.split("##");
String s61[]=s6.split("##");
String s71[]=s7.split("##");
double v1 = Double.parseDouble(s11[0]);
double v2 = Double.parseDouble(s21[0]);
double v3 = Double.parseDouble(s31[0]);
double v4 = Double.parseDouble(s41[0]);
double v5 = Double.parseDouble(s51[0]);
double v6 = Double.parseDouble(s61[0]);
double v7 = Double.parseDouble(s71[0]);
double v11 = Double.parseDouble(s11[1]);
double v21 = Double.parseDouble(s21[1]);
double v31 = Double.parseDouble(s31[1]);
double v41 = Double.parseDouble(s41[1]);
double v51 = Double.parseDouble(s51[1]);
double v61 = Double.parseDouble(s61[1]);
double v71 = Double.parseDouble(s71[1]);
double v12 = Double.parseDouble(s11[2]);
double v22 = Double.parseDouble(s21[2]);
double v32 = Double.parseDouble(s31[2]);
double v42 = Double.parseDouble(s41[2]);
double v52 = Double.parseDouble(s51[2]);
double v62 = Double.parseDouble(s61[2]);
double v72 = Double.parseDouble(s71[2]);
double v13 = Double.parseDouble(s11[3]);
double v23 = Double.parseDouble(s21[3]);
double v33 = Double.parseDouble(s31[3]);
double v43 = Double.parseDouble(s41[3]);
double v53 = Double.parseDouble(s51[3]);
double v63 = Double.parseDouble(s61[3]);
double v73 = Double.parseDouble(s71[3]);
double v14 = Double.parseDouble(s11[4]);
double v24 = Double.parseDouble(s21[4]);
double v34 = Double.parseDouble(s31[4]);
double v44 = Double.parseDouble(s41[4]);
double v54 = Double.parseDouble(s51[4]);
double v64 = Double.parseDouble(s61[4]);
double v74 = Double.parseDouble(s71[4]);
// row keys...
final String series1 = "Hospital";
final String series2 = "Software";
final String series3 = "Mobile";
final String series4 = "Telecome";
final String series5 = "Banking";
// column keys...
final String category1 = "COCOMO 81";
final String category2 = "COCOMO II(basic)";
final String category3 = "COCOMO II(Intermediate)";
final String category4 = "SLIM";
final String category5 = "Function Points";
final String category6 = "Algorithmic Cost Model";
final String category7 = "REVIREVIC";
// create the dataset...
final DefaultCategoryDataset dataset = new DefaultCategoryDataset();
dataset.addValue(v1, series1, category1);
dataset.addValue(v2, series1, category2);
dataset.addValue(v3, series1, category3);
dataset.addValue(v4, series1, category4);
dataset.addValue(v5, series1, category5);
dataset.addValue(v6, series1, category6);
dataset.addValue(v7, series1, category7);
dataset.addValue(v11, series2, category1);
dataset.addValue(v21, series2, category2);
dataset.addValue(v31, series2, category3);
dataset.addValue(v41, series2, category4);
dataset.addValue(v51, series2, category5);
dataset.addValue(v61, series2, category6);
dataset.addValue(v71, series2, category7);
dataset.addValue(v12, series3, category1);
dataset.addValue(v22, series3, category2);
dataset.addValue(v32, series3, category3);
dataset.addValue(v42, series3, category4);
dataset.addValue(v52, series3, category5);
dataset.addValue(v62, series3, category6);
dataset.addValue(v72, series3, category7);
dataset.addValue(v13, series4, category1);
dataset.addValue(v23, series4, category2);
dataset.addValue(v33, series4, category3);
dataset.addValue(v43, series4, category4);
dataset.addValue(v53, series4, category5);
dataset.addValue(v63, series4, category6);
dataset.addValue(v73, series4, category7);
dataset.addValue(v14, series5, category1);
dataset.addValue(v24, series5, category2);
dataset.addValue(v34, series5, category3);
dataset.addValue(v44, series5, category4);
dataset.addValue(v54, series5, category5);
dataset.addValue(v64, series5, category6);
dataset.addValue(v74, series5, category7);
return dataset;
}
private JFreeChart createChart(final CategoryDataset dataset) {
// create the chart...
final JFreeChart chart = ChartFactory.createBarChart(
"Chart", // chart title
"Category", // domain axis label
"Value", // range axis label
dataset, // data
PlotOrientation.VERTICAL, // orientation
true, // include legend
true, // tooltips?
false // URLs?
);
// NOW DO SOME OPTIONAL CUSTOMISATION OF THE CHART...
// set the background color for the chart...
chart.setBackgroundPaint(Color.white);
// get a reference to the plot for further customisation...
final CategoryPlot plot = chart.getCategoryPlot();
plot.setBackgroundPaint(Color.lightGray);
plot.setDomainGridlinePaint(Color.white);
plot.setRangeGridlinePaint(Color.white);
// set the range axis to display integers only...
final NumberAxis rangeAxis = (NumberAxis) plot.getRangeAxis();
rangeAxis.setStandardTickUnits(NumberAxis.createIntegerTickUnits());
// disable bar outlines...
final BarRenderer renderer = (BarRenderer) plot.getRenderer();
renderer.setDrawBarOutline(false);
// set up gradient paints for series...
final GradientPaint gp0 = new GradientPaint(
0.0f, 0.0f, Color.blue,
0.0f, 0.0f, Color.lightGray
);
final GradientPaint gp1 = new GradientPaint(
0.0f, 0.0f, Color.green,
0.0f, 0.0f, Color.lightGray
);
final GradientPaint gp2 = new GradientPaint(
0.0f, 0.0f, Color.red,
0.0f, 0.0f, Color.lightGray
);
final GradientPaint gp3 = new GradientPaint(
0.0f, 0.0f, Color.pink,
0.0f, 0.0f, Color.lightGray
);
final GradientPaint gp4 = new GradientPaint(
0.0f, 0.0f, Color.orange,
0.0f, 0.0f, Color.lightGray
);
final GradientPaint gp5 = new GradientPaint(
0.0f, 0.0f, Color.gray,
0.0f, 0.0f, Color.lightGray
);
renderer.setSeriesPaint(0, gp0);
renderer.setSeriesPaint(1, gp1);
renderer.setSeriesPaint(2, gp2);
renderer.setSeriesPaint(3, gp3);
renderer.setSeriesPaint(4, gp4);
renderer.setSeriesPaint(5, gp5);
final CategoryAxis domainAxis = plot.getDomainAxis();
domainAxis.setCategoryLabelPositions(
CategoryLabelPositions.createUpRotationLabelPositions(Math.PI / 6.0)
);
// OPTIONAL CUSTOMISATION COMPLETED.
return chart;
}
public static void main(final String[] args) {
final graph demo = new graph("Chart");
demo.pack();
RefineryUtilities.centerFrameOnScreen(demo);
demo.setVisible(true);
}
}
How to run:
note: create the following files and also add following jar files to your classpath.
algo.txt with content like 1.928##1.256##2.485##1.021##4.618
cocomo81.txt with content like 5.007##3.263##6.456##2.653##1.199
cocomoa.txt with content like 2.085##1.359##2.688##1.105##4.994, etc
please check the above code
set classpath=./lib/commons-math3-3.0.jar;./lib/jcommon-1.0.13.jar;./lib/jfreechart-1.0.13.jar;./lib/jcommon-0.9.3.jar;.
javac -d . graph.java
java cost.graph
Output:
/* scrolling of given message using threads in java applet code, implementation of banner animation in java applet code, program to display moving banner in java code */
import java.awt.*;
import java.applet.*;
/*
<applet code="animation" width="300" height="200">
</applet>
*/
public class animation extends Applet implements java.lang.Runnable
{
String msg=" Welcome to Java";
public void init()
{
setBackground(Color.yellow);
setForeground(Color.red);
}
public void Start()
{
Thread t=new Thread(this);
//this refers to the current class object.
t.start();
}
public void paint(Graphics g)
{
Font f=new Font("Arial",Font.BOLD,20);
g.setFont(f);
System.out.println("msg: "+msg);
g.drawString(msg,100,100);
}
public void run()
{
while(true)
{
try
{
char ch=msg.charAt(0);
msg=msg.substring(1,msg.length());
msg=msg+ch;
repaint();
java.lang.Thread.sleep(100);
}
catch (java.lang.Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}//while
}//run()
}//class
How to run:
javac ani.java
appletviewer ani.java
Output:
/* producer consumer problem in java using threads, producer consumer problem in java using (threads) synchronized block (wait() and notify() methods of Object class) example code, producer consumer problem in java using multithreading example, producer consumer problem in java using wait and notify */
Producer is the thread which will produce only one item at a time and it will made wait until it is consumed by the consumer.
Consumer is also a thread which will consumes only one item at a time and it is made wait until the Producer produces next item.
No Producer and no Consumer threads will produce and consume two consecutive items respectively.
class Q
{
boolean valset=false;
int n;
synchronized void put(int i)
{
try
{
if(valset)
wait();
else
{
n=i;
System.out.println("put: "+n);
valset=true;
notify();
}//else
}//try
catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}//put()
synchronized int get()
{
try
{
if(!valset)
wait();
else
{
System.out.println("put: "+n);
valset=false;
notify();
}//else
}//try
catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
return n;
}
}
//Producer class
class Producer implements java.lang.Runnable
{
Q q;
java.lang.Thread t1;
int i;
Producer(Q q)
{
this.q=q;
t1=new java.lang.Thread(this,"pt");
t1.start();
}//con
public void run()
{
System.out.println("name of the thread: "+t1.getName());
i=0;
while(true)
q.put(++i);
}//run()
}
//Consumer class
class Consumer implements java.lang.Runnable
{
Q q;
java.lang.Thread t1;
int i;
Consumer(Q q)
{
this.q=q;
t1=new java.lang.Thread(this,"ct");
t1.start();
}//con
public void run()
{
System.out.println("name of the thread: "+t1.getName());
i=0;
while(true)
i=q.get();
}//run()
}
//main class
public class demo1
{
public static void main(String arg[])
{
Q q=new Q();
Producer pro=new Producer(q);
Consumer con=new Consumer(q);
}
}
how to run:
javac demo1.java
java demo1
note: press ctrl+c to stop
Output:
/* Client and Server Socket example code in java,
Client-Server Programming in Java code, server and client program in java, Server Socket example code */
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
class ServerSocketDemo
{
public static void main(String []args)
{
java.net.ServerSocket ss=null;
java.io.PrintWriter pw = null;
java.io.BufferedReader br = null;
int i=0;
try
{
//server running at 40000 port number
ss = new java.net.ServerSocket(40000);
}
catch(java.lang.Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Exception in Server while creating connection"+e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.print("Server is ready");
while (true)
{
System.out.println (" Waiting for connection....");
java.net.Socket s=null;
try
{
System.out.println("connection "+s+ "\n printwriter "+pw+"\n bufferedreader "+br);
s = ss.accept();
System.out.println("Connection established with client");
pw = new java.io.PrintWriter(s.getOutputStream());
br = new java.io.BufferedReader(new java.io.InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
System.out.println("connection "+s+ "\n printwriter "+pw+"\n bufferedreader "+br);
i = new Integer(br.readLine());
System.out.println("i is "+i);
}
catch(java.lang.Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Exception in Server "+e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Connection established with "+s);
i*=i;
pw.println(i);
try
{
pw.close();
br.close();
}
catch(java.lang.Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Exception while closing streams");
}
}
}
}
//Client Socket example code
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
class ClientSocketDemo
{
public static void main(String []arga) throws java.lang.Exception
{
java.net.Socket s = null;
java.io.PrintWriter pw = null;
java.io.BufferedReader br = null;
System.out.println("Enter a number one digit");
int i=(System.in.read()-48); // will read only one character
System.out.println("Input number is "+i);
try
{
//sending request to the server running at ip 192.16.0.100 and port 40000
s = new java.net.Socket("192.168.0.100",40000);
System.out.println(s);
pw = new java.io.PrintWriter(s.getOutputStream());
System.out.println(pw);
br = new java.io.BufferedReader(new java.io.InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
System.out.println(br);
System.out.println("Connection established, streams created");
}
catch(java.lang.Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Exception in Client "+e);
}
pw.println(i);
pw.flush();
System.out.println("Data sent to server");
String str = br.readLine();
System.out.println("The square of "+i+" is "+str);
}
}
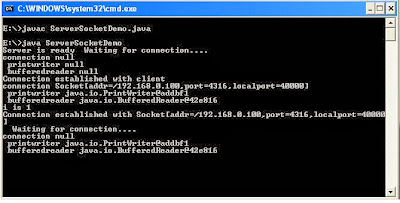
Output:
/* Roman To Decimal conversion in java example code, roman numeral to decimal java program, java program for converting decimal to roman */
public class RomanToDecimal
{
public static void romanToDecimal(String romanNumber)
{
//Initialization
int decimal = 0;
int lastNumber = 0;
//operation to be performed on upper cases even if user enters roman values in lower case chars
String romanNumeral = romanNumber.toUpperCase();
for (int x = romanNumeral.length() - 1; x >= 0 ; x--)
{
//getting each character to convert
char convertToDecimal = romanNumeral.charAt(x);
//choosing a number
switch (convertToDecimal) {
case 'M':
//if char is equals to 'M' then the number is '1000'
decimal = processDecimal(1000, lastNumber, decimal);
lastNumber = 1000;
break;
case 'D':
//if char is equals to 'D' then the number is '500'
decimal = processDecimal(500, lastNumber, decimal);
lastNumber = 500;
break;
case 'C':
//if char is equals to 'C' then the number is '100'
decimal = processDecimal(100, lastNumber, decimal);
lastNumber = 100;
break;
case 'L':
//if char is equals to 'L' then the number is '50'
decimal = processDecimal(50, lastNumber, decimal);
lastNumber = 50;
break;
case 'X':
//if char is equals to 'X' then the number is '10'
decimal = processDecimal(10, lastNumber, decimal);
lastNumber = 10;
break;
case 'V':
//if char is equals to 'V' then the number is '5'
decimal = processDecimal(5, lastNumber, decimal);
lastNumber = 5;
break;
case 'I':
//if char is equals to 'I' then the number is '1'
decimal = processDecimal(1, lastNumber, decimal);
lastNumber = 1;
break;
}
}
//displaying output
System.out.println("roman number: "+romanNumber+"\ndecimal number: "+decimal);
}
public static int processDecimal(int decimal, int lastNumber, int lastDecimal)
{
//processing decimals
if (lastNumber > decimal)
{
return lastDecimal - decimal;
} else
{
return lastDecimal + decimal;
}
}
//main method
public static void main(java.lang.String args[])
{
romanToDecimal("xi");
}
}
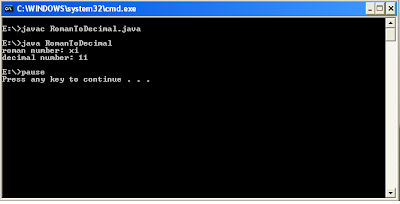
Output:
E:\>javac RomanToDecimal.java
E:\>java RomanToDecimal
roman number: xi
decimal number: 11
/* how to do highlight on string in java code, java highlight word in string */
here is a sample code
String startTag = "<b><font size='3' color='blue'>";
String startTag1 = "<font size='2' color='blue'>";
String endTag1 = "</font>";
String endTag = "</font></b>";
//here 'al' is arraylist which contains some elements
for(int i1=0;i1<ary1.length;i1++)
{
if(al.contains(ary1[i1].toLowerCase().trim()))
{
//flag=1;
hResult.append(startTag);
hResult.append(ary1[i1]+" ");
hResult.append(endTag);
}
else
{
//flag=flag;
hResult.append(startTag1);
hResult.append(ary1[i1]+" ");
hResult.append(endTag1);
}
}
here print the output.
output:


+synchronized+block.jpg)