import java.util.Vector;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/*Java program to solve Producer Consumer problem using wait and notify
*/
public class ProducerConsumer {
public static void main(String vals[]) {
java.util.Vector sharedQueue = new java.util.Vector();
int size = 4;
java.lang.Thread prodThread = new java.lang.Thread(new Producer(sharedQueue, size), "Producer");
java.lang.Thread consThread = new java.lang.Thread(new Consumer(sharedQueue, size), "Consumer");
prodThread.start();
consThread.start();
}
}
class Producer implements java.lang.Runnable {
private final java.util.Vector sharedQueue;
private final int SIZE;
public Producer(java.util.Vector sharedQueue, int size) {
this.sharedQueue = sharedQueue;
this.SIZE = size;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
System.out.println("Produced: " + i);
try {
produce(i);
} catch (java.lang.InterruptedException e) {
Logger.getLogger(Producer.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, e);
}
}
}
private void produce(int i) throws InterruptedException {
//wait if queue is full
while (sharedQueue.size() == SIZE) {
synchronized (sharedQueue) {
System.out.println("Queue is full " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ " is waiting , size: " + sharedQueue.size());
sharedQueue.wait();
}
}
//producing element and notify consumers
synchronized (sharedQueue) {
sharedQueue.add(i);
sharedQueue.notifyAll();
}
}
}
class Consumer implements java.lang.Runnable {
private final java.util.Vector sharedQueue;
private final int SIZE;
public Consumer(java.util.Vector sharedQueue, int size) {
this.sharedQueue = sharedQueue;
this.SIZE = size;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
System.out.println("Consumed: " + consume());
java.lang.Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(Consumer.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}
}
}
private int consume() throws InterruptedException {
//wait if queue is empty
while (sharedQueue.isEmpty()) {
synchronized (sharedQueue) {
System.out.println("Queue is empty " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ " is waiting , size: " + sharedQueue.size());
sharedQueue.wait();
}
}
//Otherwise consume element and notify waiting producer
synchronized (sharedQueue) {
sharedQueue.notifyAll();
return (Integer) sharedQueue.remove(0);
}
}
}
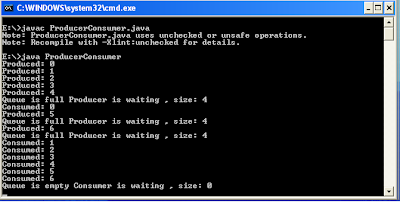
output:
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/*Java program to solve Producer Consumer problem using wait and notify
*/
public class ProducerConsumer {
public static void main(String vals[]) {
java.util.Vector sharedQueue = new java.util.Vector();
int size = 4;
java.lang.Thread prodThread = new java.lang.Thread(new Producer(sharedQueue, size), "Producer");
java.lang.Thread consThread = new java.lang.Thread(new Consumer(sharedQueue, size), "Consumer");
prodThread.start();
consThread.start();
}
}
class Producer implements java.lang.Runnable {
private final java.util.Vector sharedQueue;
private final int SIZE;
public Producer(java.util.Vector sharedQueue, int size) {
this.sharedQueue = sharedQueue;
this.SIZE = size;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
System.out.println("Produced: " + i);
try {
produce(i);
} catch (java.lang.InterruptedException e) {
Logger.getLogger(Producer.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, e);
}
}
}
private void produce(int i) throws InterruptedException {
//wait if queue is full
while (sharedQueue.size() == SIZE) {
synchronized (sharedQueue) {
System.out.println("Queue is full " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ " is waiting , size: " + sharedQueue.size());
sharedQueue.wait();
}
}
//producing element and notify consumers
synchronized (sharedQueue) {
sharedQueue.add(i);
sharedQueue.notifyAll();
}
}
}
class Consumer implements java.lang.Runnable {
private final java.util.Vector sharedQueue;
private final int SIZE;
public Consumer(java.util.Vector sharedQueue, int size) {
this.sharedQueue = sharedQueue;
this.SIZE = size;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
System.out.println("Consumed: " + consume());
java.lang.Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(Consumer.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}
}
}
private int consume() throws InterruptedException {
//wait if queue is empty
while (sharedQueue.isEmpty()) {
synchronized (sharedQueue) {
System.out.println("Queue is empty " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ " is waiting , size: " + sharedQueue.size());
sharedQueue.wait();
}
}
//Otherwise consume element and notify waiting producer
synchronized (sharedQueue) {
sharedQueue.notifyAll();
return (Integer) sharedQueue.remove(0);
}
}
}
output: